HEE Guidelines 2016: A Brief Summary

On 8th January 2016 Health Education England (HEE) published Part Two of their Qualification Requirements for Delivery of Cosmetic Procedures. Below is a summary of the background of and latest changes to these guidelines as far as they will affect those who train or deliver injectable treatments (e.g. Botulinum Toxins and dermal fillers).
Part Two of the HEE Guidelines for Cosmetic Procedures builds on the 2015 requirements for cosmetic training.
‘Part One sets out the qualification requirements, which include guidance on the application of the requirements for different groups of practitioners working in the cosmetics or aesthetic field. Part Two describes the second and final phase of the project to produce the detailed qualification requirements for delivery of non-surgical cosmetic interventions and hair restoration surgery.’ – HEE 2016.
Currently HEE requirements are best-practice guidelines and do not yet represent statute law.
HEE guidelines: a background
The current landscape the HEE guidelines are responding to, involves:
– no legal restrictions on who may perform cosmetic procedures
– no qualification requirements
– an absence of accredited training courses in an increasingly lucrative industry (worth over £3.6 billion).

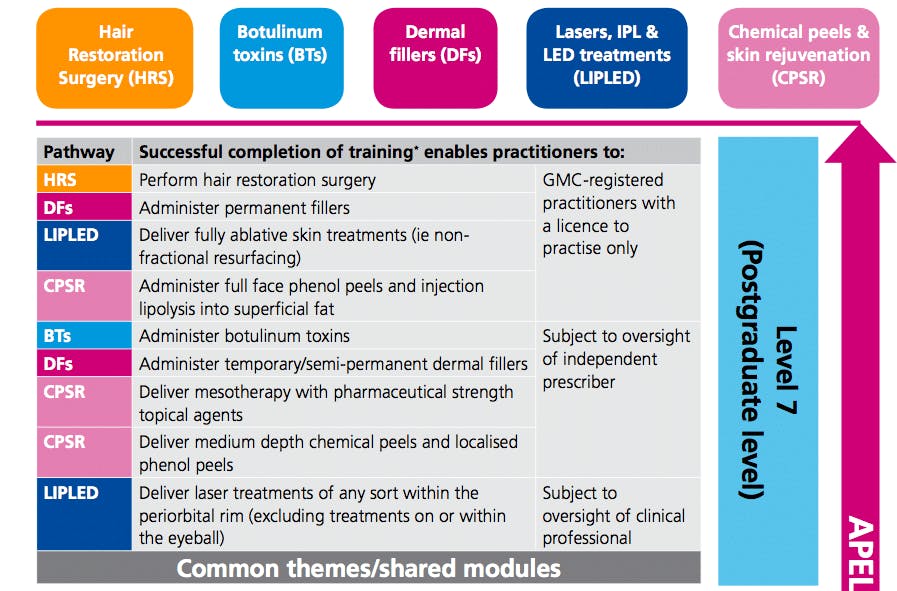
Five main modalities covered by the HEE requirements
1. Botulinum Toxin
2. Dermal Fillers
3. Lasers, IPL and LED Treatments
4. Chemical Peel / Skin Rejuvenation
5. Hair Restoration
Key points about the requirements
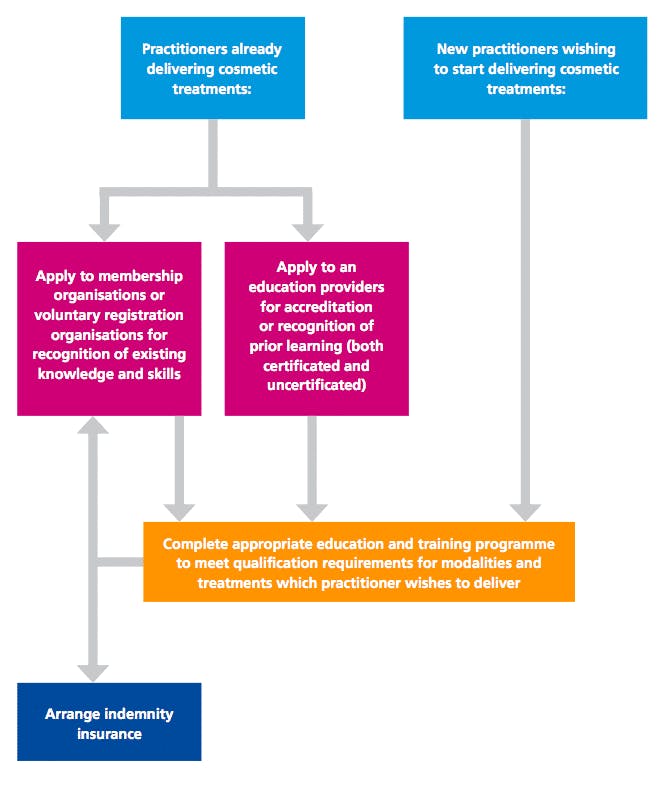
The requirements apply to all practitioners, regardless of previous training and professional background.
- All groups will be required to:
- undertake additional education and training to be able to deliver cosmetic interventions, or
- formally demonstrate that they already meet the qualification requirements. - Recognition of Prior Learning: Practitioners who have already completed training will be able to apply for formal recognition from an accredited cosmetic training provider. Very short courses, e.g. 1-2 days in duration, will not meet the requirements for Recognition of Prior Learning.
- A joint council is to be formed, which will take ownership of cosmetic industry standards for education and training.
- HEE do not expect practitioners to stop practicing whilst new qualification frameworks are in development. ‘Although adoption of the new requirements will be voluntary at this stage, it is recommended that the qualification requirements be adopted as best practice and accepted as the standard that the industry should adopt improve public safety and raise standards of practice and professionalism’
- Practitioners should take care to select courses which promote safe practice.
- For Practitioners
What remains unchanged in the HEE Guidelines for Cosmetic Procedures
- As in Part One, only GMC-registered practitioners may administer permanent fillers.
- Dermal Fillers are still classed as a medical device and don’t require a prescription.
- HEE agrees with GMC, GDC and NMC guidance on face-to-face consultations before prescribing. And, as in Part One, the following groups are able to prescribe botulinum toxins for cosmetic purposes:
- Doctors and dentists
- Pharmacist independent prescribers
- Nurse and midwife independent prescribers - Dermatologists and plastic surgeons are exempt from some areas of additional theoretical learning.
- Following completion of training, practitioners are encouraged to identify a professional colleague or mentor with whom they can discuss complex clinical or ethical developments.
What has changed in the guidelines
Clinical oversight required for a practitioner
Initially high for someone who has just completed their training (AKA oversight for botulinum toxin and dermal filler treatments will require oversight by an independent prescriber), but it will be a matter of clinical and professional judgement to determine the degree of oversight required.
Education
Practitioners do not require a clinically relevant qualification before they apply for training to deliver cosmetic procedures. In other words, you don’t necessarily need a medical degree.
However, practitioners performing injectable treatments (botulinum toxins & dermal fillers) amongst others (below) will now be required to study to at least one postgraduate degree level (where previously this was specified as undergraduate level).
The deadline is September 2018 for completion of this postgraduate training.
What kind of theoretical learning will be required?
Below are example learning requirements for cosmetic knowledge from the HEE Requirements Part One.
- Understanding of relevant dermatological conditions/diseases, e.g. cherry angioma, spider naevus, actinic lentigo, melasma, benign dyschromias related to sun damage, acne, hirsutism, rosacea
- Understanding of common health conditions which may affect treatment, e.g. diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease/stroke, autoimmune disease, immunocompromised patients, those with transmissible infections, alcohol/drug abuse
- Ability to take photographs both pre- and post-treatment photography and understand how they should be used.
Example Learning Requirements for Botulinum Toxins (HEE Requirements Part One):
- In depth understanding of facial and neck anatomy including relevant vessels, nerves and muscles
- Identification of contraindications for use, e.g. pregnancy, breast feeding, history of neuromuscular disorder
- Understanding of potential risks including facial asymmetry, ptosis, dry eyes, drooling, lip drooping, difficulty speaking or swallowing, dry mouth, respiratory distress.
Example Learning Requirements for Dermal Fillers (HEE Requirements Part One):
- In depth understanding of facial anatomy including relevant vessels, nerves, muscles and fat pads
- Understanding of biochemistry, pharmacology of various types of dermal filler: permanent, semi-permanent and temporary; replacement vs stimulatory; with or without local anaesthetic
- Understanding and recognition of specific adverse events including hypersensitivity, biofilm, granuloma, nodule formation with suppuration and abscess formation and treat or refer on appropriately.
For Training Courses
What remains unchanged in the guidelines
- Training courses must have their own degree awarding powers or be OfQual-regulated, or work in partnership with such organisations.
- A minimum of 50% of the curriculum must be devoted to the development of practical skills:
- Botulinum Toxin: students must observe 10 treatments, followed by 10 supervised treatments
- Dermal Fillers: students must observe 10 treatments, followed by 10 supervised treatments
- Delegates must subsequently pass a rigorous and standardised assessment.
Supervisors must be able to provide clinical oversight and be be proficient with injectables (a minimum of 3 years experience).
It is up to education providers to determine the detailed learning outcomes for individual courses or modules of study and the number and size of required modules.
Harley Academy’s learning materials and courses have been specifically designed using the HEE guidelines. Consider taking our postgraduate qualification, which takes you from a BOTOX and Dermal Fillers foundation training day all the way to a fully qualified aesthetic practitioner with the added benefits our unique course provides, including peer-to-peer networking and business training.
Key resources:
HEE Guidelines for Cosmetic Procedures Part 1
HEE Guidelines for Cosmetic Procedures Part 2
All information correct at the time of publication. Last updated: 4 December 2020
Download our full prospectus
Browse all our injectables, dermal fillers and cosmetic dermatology courses in one document
By submitting this form, you agree to receive marketing about our products, events, promotions and exclusive content. Consent is not a condition of purchase, and no purchase is necessary. Message frequency varies. View our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions
Attend our FREE open evening
If you're not sure which course is right for you, let us help
Join us online or in-person at our free open evening to learn more
Our Partners













STAY INFORMED
Sign up to receive industry news, careers advice, special offers and information on Harley Academy courses and services

